 打印本文
打印本文  关闭窗口
关闭窗口
教学目标
1.知识目标
(1)New words and phrase: lift, up and down, busy, team, center, popular, quite, month, village, strong, soccer, Gum Tree, Ashland, Richmond
(2)语法知识:现在进行时,一般现在时, be going to 结构表示将来要发生的动作,形容词和副词的比较级和最高级,提建议的表达方法,表示需要, 询问方向, 指点方向.
(3)语音知识: /iз/ea, ear, /εз/ air ,ear,ere
2.能力目标
(1)使学生能够熟练掌握1-7单元的语法项目并能灵活运用.
(2)使学生能够听懂与课文难度相当的听力材料,并能根据上下文判断生词的含义.
(3)使学生能够熟练运用于1-7单元交际用语并根据不同情景进行对话.
3.德育目标
培养学生良好的学习习惯和学习兴趣.
通过教学,教育学生热爱运动,积极参与,德智体全面发展。
通常学习,让学生感受到体育运动给大家带来的欢乐和愉悦。
教学建议
教材分析
本单元是复习单元,它综合了从第一单元到第六单元的所有语法知识和相关交际项目。Lesson 25主要是复习现在进行时和be going to 结构要求学生能区分两种结构在意义上和形式上的区别,并能根据情景熟练进行交际运用。Lesson 26是一篇阅读材料,在提高阅读能力的同时,重点复习了一般现在时的句子结构。Lesson 27主要是复习提建议、邀请和介绍事物的相关交际用语,Lesson 28主要是复习有关问路和指路的交际用语。教师在教学过程中除了对具体的语言项目进行复习以外应注重提高学生综合运用语言的能力。
复习引导
本单元的教学内容是复习1—7 单元的所有语法项目和交际用语。教师应对一至六单元的教学内容进行归纳和总结,使教学内容条理化,系统化。在教学过程中还应多设计一些综合性的练习以提高学生综合运用语言的能力。可采用比较法,归纳法。要求学生们巩固已学的时态,及如何提建议回答的各种句型。
口语教学建议
本单元的口语主要安排在第25课和第28课中,但其它课文中也有体现,教师应深入挖掘教材,多给学生创造口语练习机会,提高学生口语的能力。
(1)在Lesson 25的教学中,教师应注意练习的设计应体现阶段性和层次性, Part one 教师可先准备四种单词卡,不同种单词卡上分别写上人称,(如I, you, they, he, she, we, Tom, Peter and Mary. e.g.),动词的现在分词形式(如swimming, flying ,listening, e.g.),地点(如onthehill,intheswimmingpool,inthesky)。在教学时先将学生分组,要求小组成员到讲台前选取单词卡片并组成句子,最后,教师对组句多的小组进行奖励。此练习主要是练习学生对现在进行时句子结构的掌握情况。待学生句子结构熟练掌握之后,再出示书中的图片,按照教科书进行看图说话练习。最后,教师可以对be going to 结构和现在进行时进行比较.找出异同进行比较。
(2)在Lesson 26的教学过程中,教师可以在学生读完文章之后就课后的问题进行讨论,以锻炼学生的口语表达能力。教师可以组织学生把课文改编成一个小型的对话,运用一般现在时简单讲述Paul的一天,如下:
A: Hello!
B: Hello!How are you?
A: Fine, thank you. And you?
B:I am fine, too.
A: Do you know Paul?
B: Only a little. He is a Canadian.
A: Yes, he lives in the city of Toronto. His flat is on the 15th floor.
B: Does he have to use the lift to go up and down?
A: Yes, Paul is a busy man. He has to get up early everyday. The bus stop is in front of a cinema. It is about two hundred meters away from his home.
B: How does he go to work?
A: He usually catches the No.11bus to work, but sometime he goes by train.
B: When does he start and finish his work?
A: He starts to work at half past eight and finishes at a quarter to five.
B: What does Paul like?
A: He likes doing sports after work. He is also on the city basketball team.
B: Is he good at the basketball?
A: Certainly. He is the shortest man on the team, but he is the fastest.
B: When does he come back?
A: He comes back at a quarter past five. He gets into the lift and goes up to the twelfth floor. Then he gets out of the lift and walks up to the fifteenth floor.
B: Why does he not use the lift for the last three floors?
A: Because he is the shortest. He is not taller enough to touch the lift button of the eighteenth floor.
(3)在第28 课的教学过程中,在完成文中对话后教师可以组织学生以两人为一组分别向对方介绍如何去自己家。
Lesson28的地图可扫描成图片,让学生进行对话,现给出一些对话如下:
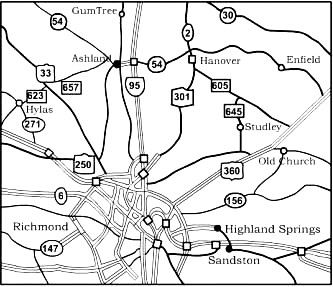
—Now, you know Ashland is about 8 miles from Richmond. Then, look at the map. How far is it from Gum Tree?
—Perhaps about 3 miles.
—Which town do you think is also about 8 miles away from Richmond?
—I think both Hanover and Old Church are.
—Which road would you take if you travel from Old Church to Richmond: No.360 or No.156?
—I think I would take No.360.
—Why?
—It’s wider and so it’s faster.
听力训练建议
(1)在本单元的听力教学中,教师可以拓展学生听力范围,除了已有的两个听力材料需要精听外,在讲阅读文章时也可以先听一遍文章,设计两个问题让学生回答。也可以把英文歌曲也当成听力材料来讲。精听和泛听要结合。
(2)听,说也要结合。教师可以在讲完文中的对话后,播放录音的问句,让学生说答句,也可说答句让学生就答句提问。
课文提示
Lesson 26课文最后一句:Why doesn’t he use the lift for the last three floors?可以给学生下面几种情况作为答案。
Because he wants to take more exercise by walking up the last three floors. Or because the lift is designed or made to go as up as the 12th floor. He has to walk up the rest of the three floors.
同时让学生自己来猜测一下还有别的原因,发挥学生的丰富想象,以激发学生的兴趣。
We live in a place called Gum three.我们住在一个叫做桉树村的地方。
a place called …一个叫做……的地方。Called Gum Tree 在句中是过去分词短语做定语,修饰a place。例如:
I have a friend called Jack.我有一个朋友叫杰克。
When I was young, I lived in a city called Gui yang.
例I know a woman ____ “Big Sister”.
A. call B. calls C. called D. to call
思路分析
英语中常用过去分词短语作后置定语来修饰前面的名词。We have three students named Yang in our class. (我们班上有三个姓杨的同学。)
答案:C
Aren’t all balls round? 难道所有的球不都是圆形的吗?
(1)该句属于否定疑问句,表示说话人的惊喜、指责、惊讶等语气,通常译作“难道不……吗?” 又如:Don’t you know me? 难道你不认识我吗?
(2)not与all, every等含全体概念的词连用时,表示部分否定。例如:
Not every student wants to go to the park. 并不是每个学生都想到公园去。
Every girl doesn’t like wearing skirts.并非所有女孩都喜欢穿裙子。
(=Not every girl likes wearing skirts)
(3)若要表示全否定,即要说“都不……”,则应用一些本身便表示全否定的词,如: nobody, nothing, none等。如:
Nothing is wrong with your eyes.你的眼睛没问题。
Nobody is at home today.今天没有一个人在家。
辨析also与 too
also和too都可表示“也”,一般用于肯定句和疑问句中,不用于否定句。在否定句中,表示“也”用either. also常放在句中,其位置在行为动词之前,系动词be之后。句中如有助动词或情态动词时,一般放在助动词或情态动词之后。too常放在句末,它前面可用逗号,也可不用。若置于句中,其前后均有逗号。如:
Her sister is also a student. 她姐姐也是一个学生。
He can also speak Japanese. 他也能说日语。
Would you like to go there, too?你也想去那儿吗?
He, too, likes playing football.他也喜欢踢足球。
辨析city与 town
city一般指“城市、都市”,而town指“城镇”,比city小,又作countryside (乡下)的相对语。如:
the city of Shanghai 上海市,the city of Jinan. 济南市。
town(镇)比village(村)大,在英国town比city用得广。如:
go to town(从乡下)到镇上去;(从郊处)到市区去。
Be in town进城了 Be out of town离城了
Go town to do some shopping 到闹市去买东西
此文章共有6页 第 1 2 3 4 5 6 页
 打印本文
打印本文  关闭窗口
关闭窗口